| Title: NASA pics | |
| Grapevine50sRoost > ~GENERAL~ > GENERAL DISCUSSION | Go to subcategory: |
| Author | Content |
|
zxxlyzq
|
|
|
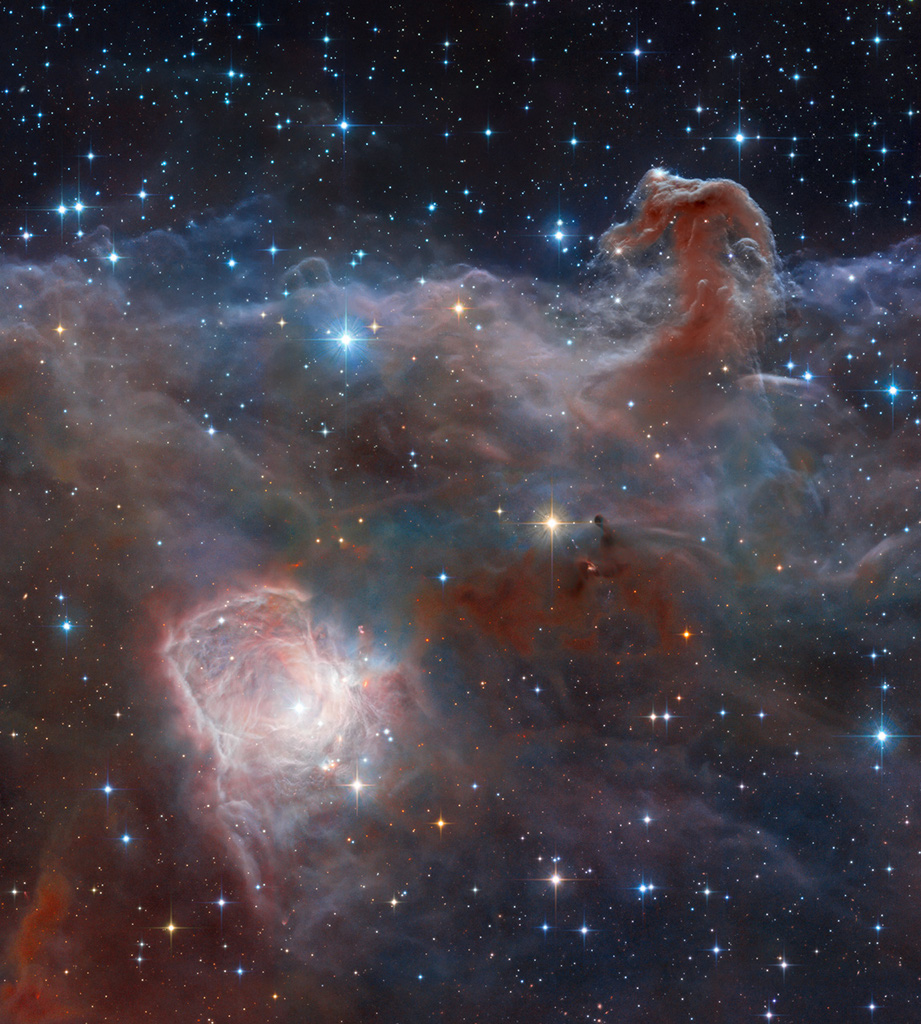
Date Posted:09/03/2018 12:10 PMCopy HTML Composition and Processing: Robert Gendler Image Data: ESO, VISTA, HLA, Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA) Explanation: Combined image data from the massive, ground-based VISTA telescope and the Hubble Space Telescope was used to create this wide perspective of the interstellar landscape surrounding the famous Horsehead Nebula. Captured at near-infrared wavelengths, the region's dusty molecular cloud sprawls across the scene that covers an angle about two-thirds the size of the Full Moon on the sky. Left to right the frame spans just over 10 light-years at the Horsehead's estimated distance of 1,600 light-years. Also known as Barnard 33, the still recognizable Horsehead Nebula stands at the upper right, the near-infrared glow of a dusty pillar topped with newborn stars. Below and left, the bright reflection nebula NGC 2023 is itself the illuminated environs of a hot young star. Obscuring clouds below the base of the Horsehead and on the outskirts of NGC 2023 show the tell-tale far red emission of energetic jets, known as Herbig-Haro objects, also associated with newborn stars. |
|
|
Rockymz
|
Share to:





 #1201
#1201
|
|
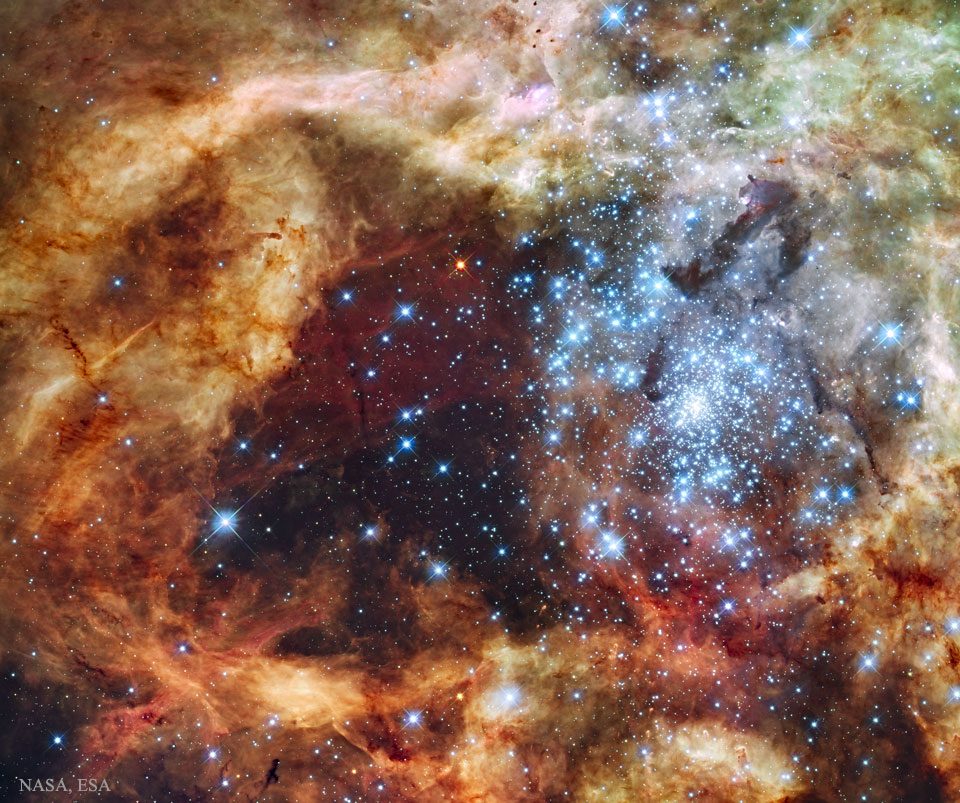
Re:NASA pics Date Posted:10/01/2021 7:29 AMCopy HTML Image Credit: NASA, ESA, & F. Paresce (INAF-IASF), R. O'Connell (U. Virginia) et al. Explanation: In the center of nearby star-forming region lies a huge cluster containing some of the largest, hottest, and most massive stars known. These stars, known collectively as star cluster R136, part of the Tarantula Nebula, were captured in the featured image in visible light in 2009 through the Hubble Space Telescope. Gas and dust clouds in the Tarantula Nebula, have been sculpted into elongated shapes by powerful winds and ultraviolet radiation from these hot cluster stars. The Tarantula Nebula lies within a neighboring galaxy known as the Large Magellanic Cloud and is located a mere 170,000 light-years away. |
|
|
Rockymz
|
Share to:





 #1202
#1202
|
|
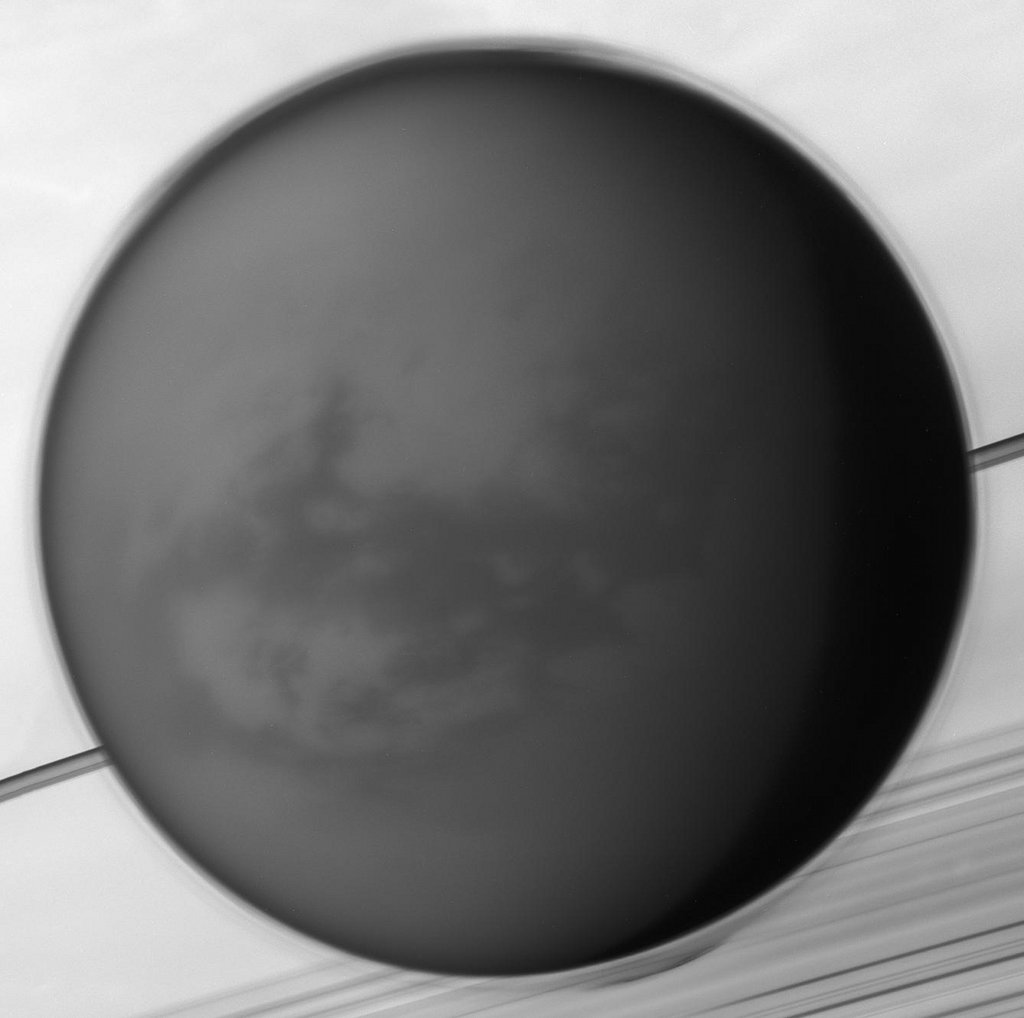
Re:NASA pics Date Posted:09/01/2021 7:35 AMCopy HTML Image Credit: NASA, JPL-Caltech, Space Science Institute Explanation: Like Earth's moon, Saturn's largest moon Titan is locked in synchronous rotation. This mosaic of images recorded by the Cassini spacecraft in May of 2012 shows its anti-Saturn side, the side always facing away from the ringed gas giant. The only moon in the solar system with a dense atmosphere, Titan is the only solar system world besides Earth known to have standing bodies of liquid on its surface and an earthlike cycle of liquid rain and evaporation. Its high altitude layer of atmospheric haze is evident in the Cassini view of the 5,000 kilometer diameter moon over Saturn's rings and cloud tops. Near center is the dark dune-filled region known as Shangri-La. The Cassini-delivered Huygens probe rests below and left of center, after the most distant landing for a spacecraft from Earth. |
|
|
Rockymz
|
Share to:





 #1203
#1203
|
|
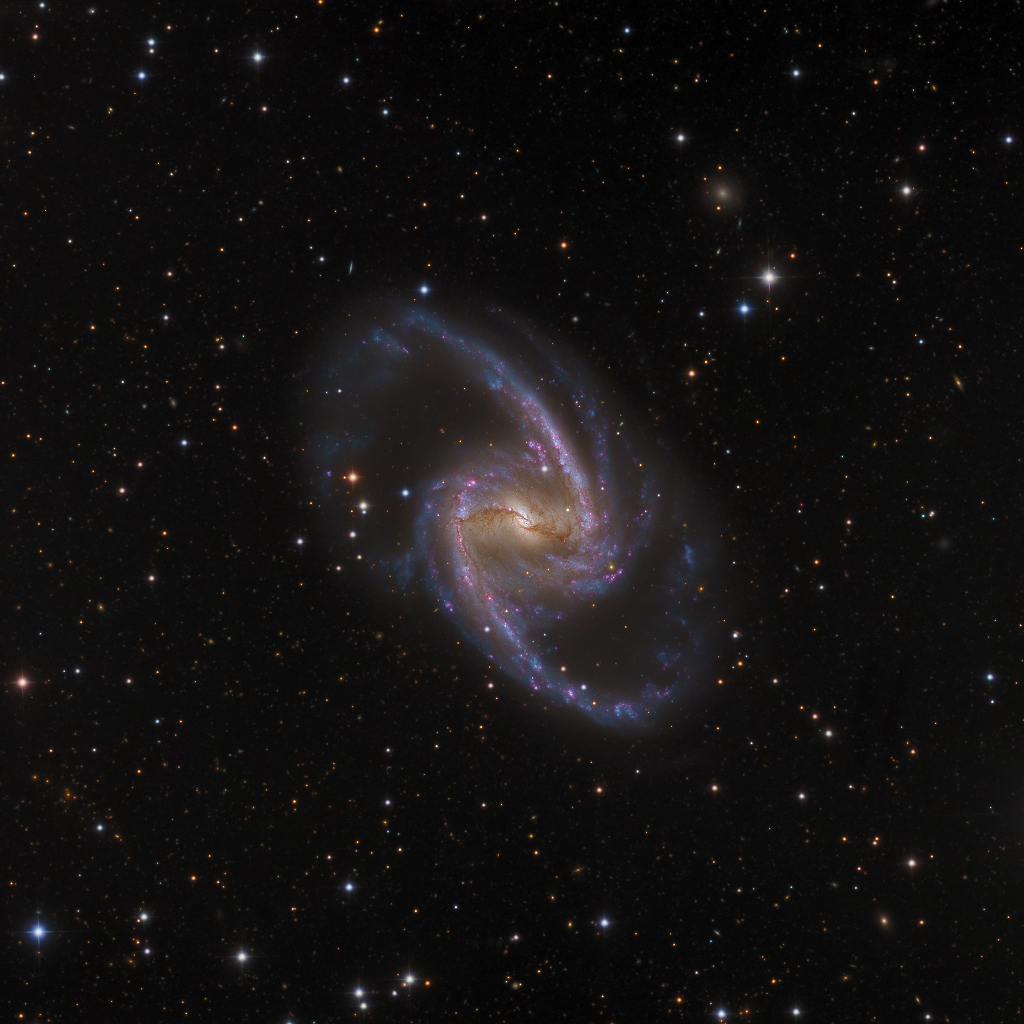
Re:NASA pics Date Posted:08/01/2021 7:46 AMCopy HTML Image Credit & Copyright: Mike Selby, Leonardo Orazi Explanation: Barred spiral galaxy NGC 1365 is truly a majestic island universe some 200,000 light-years across. Located a mere 60 million light-years away toward the chemical constellation Fornax, NGC 1365 is a dominant member of the well-studied Fornax Cluster of galaxies. This impressively sharp color image shows the intense, reddish star forming regions near the ends of central bar and along the spiral arms, with details of the obscuring dust lanes cutting across the galaxy's bright core. At the core lies a supermassive black hole. Astronomers think NGC 1365's prominent bar plays a crucial role in the galaxy's evolution, drawing gas and dust into a star-forming maelstrom and ultimately feeding material into the central black hole. |
|
|
zxxlyzq
|
Share to:





 #1204
#1204
|
|
Re:NASA pics Date Posted:07/01/2021 8:47 AMCopy HTML https://apod.nasa.gov/apod/ap210107.html |
|
|
Rockymz
|
Share to:





 #1205
#1205
|
|
Re:NASA pics Date Posted:07/01/2021 7:52 AMCopy HTML Image Credit & Copyright: Miloslav Druckmuller, Andreas Moller, (Brno University of Technology), Explanation: Along a narrow path crossing southern South America through Chile and Argentina, the final New Moon of 2020 moved in front of the Sun on December 14 in the year's only total solar eclipse. Within about 2 days of perigee, the closest point in its elliptical orbit, the New Moon's surface is faintly lit by earthshine in this dramatic composite view. The image is a processed composite of 55 calibrated exposures ranging from 1/640 to 3 seconds. Covering a large range in brightness during totality, it reveals the dim lunar surface and faint background stars, along with planet-sized prominences at the Sun's edge, an enormous coronal mass ejection, and sweeping coronal structures normally hidden in the Sun's glare. Look closely for an ill-fated sungrazing Kreutz family comet (C/2020 X3 SOHO) approaching from the lower left, at about the 7 o'clock position. In 2021 eclipse chasers will see an annular solar eclipse coming up on June 10. They'll have to wait until December 4 for the only total solar eclipse in 2021 though. That eclipse will be total along a narrow path crossing the southernmost continent of Antarctica. |
|
|
Rockymz
|
Share to:





 #1206
#1206
|
|
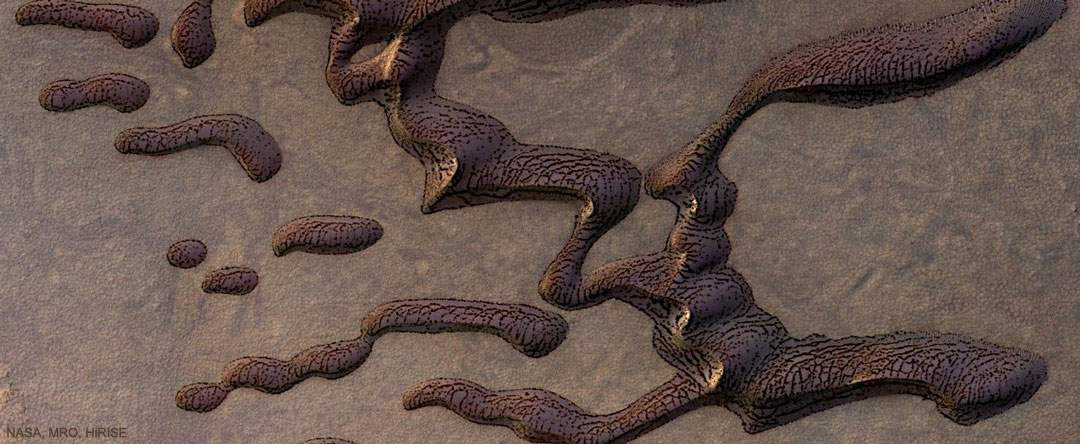
Re:NASA pics Date Posted:06/01/2021 9:01 AMCopy HTML Image Credit: HiRISE, MRO, LPL (U. Arizona), NASA; Processing: Włodek Głażewski; Text: Alex R. Howe (NASA/USRA, Reader's History of SciFi Podcast) Explanation: Why are these sand dunes on Mars striped? No one is sure. The featured image shows striped dunes in Kunowsky Crater on Mars, photographed recently with the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter’s HiRISE Camera. Many Martian dunes are known to be covered unevenly with carbon dioxide (dry ice) frost, creating patterns of light and dark areas. Carbon dioxide doesn’t melt, but sublimates, turning directly into a gas. Carbon dioxide is also a greenhouse material even as a solid, so it can trap heat under the ice and sublimate from the bottom up, causing geyser-like eruptions. During Martian spring, these eruptions can cause a pattern of dark defrosting spots, where the darker sand is exposed. The featured image, though, was taken during Martian autumn, when the weather is getting colder – making these stripes particularly puzzling. One hypothesis is that they are caused by cracks in the ice that form from weaker eruptions or thermal stress as part of the day-night cycle, but research continues. Watching these dunes and others through more Martian seasons may give us more clues to solve this mystery. |
|
|
Rockymz
|
Share to:





 #1207
#1207
|
|
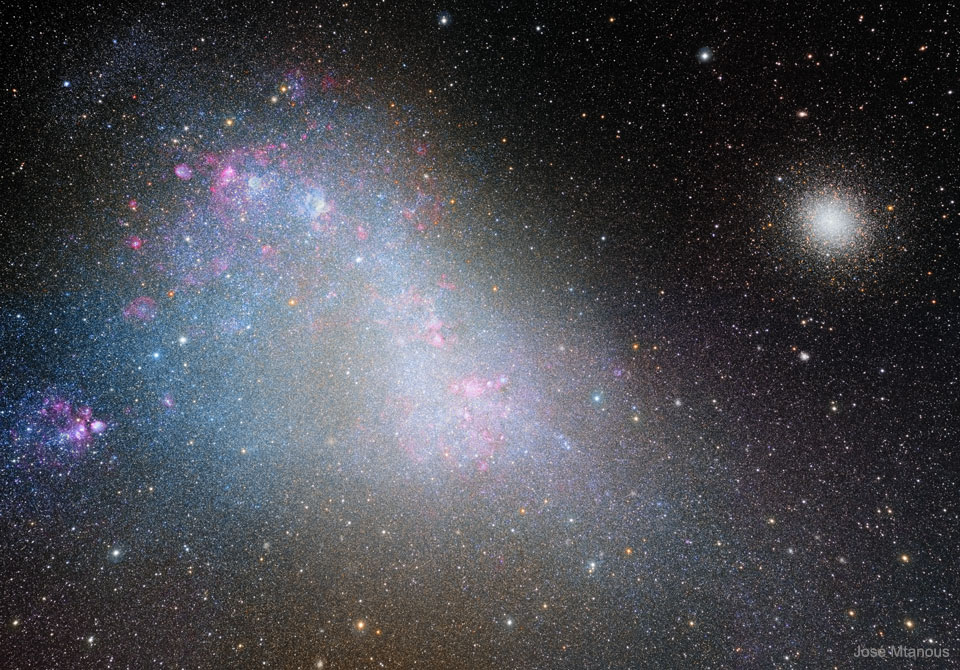
Re:NASA pics Date Posted:05/01/2021 7:31 AMCopy HTML Image Credit & Copyright: José Mtanous Explanation: What is the Small Magellanic Cloud? It has turned out to be a galaxy. People who have wondered about this little fuzzy patch in the southern sky included Portuguese navigator Ferdinand Magellan and his crew, who had plenty of time to study the unfamiliar night sky of the south during the first circumnavigation of planet Earth in the early 1500s. As a result, two celestial wonders easily visible for southern hemisphere skygazers are now known in Western culture as the Clouds of Magellan. Within the past 100 years, research has shown that these cosmic clouds are dwarf irregular galaxies, satellites of our larger spiral Milky Way Galaxy. The Small Magellanic Cloud actually spans 15,000 light-years or so and contains several hundred million stars. About 210,000 light-years away in the constellation of the Tucan (Tucana), it is more distant than other known Milky Way satellite galaxies, including the Sagittarius Dwarf galaxy and the Large Magellanic Cloud. This sharp image also includes the foreground globular star cluster 47 Tucanae on the right. |
|
|
Rockymz
|
Share to:





 #1208
#1208
|
|
Re:NASA pics Date Posted:04/01/2021 8:21 AMCopy HTML
Image Credit: NASA, ESA, Hubble, ESO, Amateur Data; Processing & Copyright: Robert Gendler & Roberto Colombari Explanation: Image data from the Hubble Space Telescope, the European Southern Observatory, and small telescopes on planet Earth are combined in this magnificent portrait of face-on spiral galaxy Messier 61 (M61). A mere 55 million light-years away in the Virgo Cluster of Galaxies, M61 is also known as NGC 4303. It's considered to be an example of a barred spiral galaxy similar to our own Milky Way. Like other spiral galaxies, M61 also features sweeping spiral arms, cosmic dust lanes, pinkish star forming regions, and young blue star clusters. The bright galactic core is offset to the left in this 50 thousand light-year wide close-up. |
|
|
Rockymz
|
Share to:





 #1209
#1209
|
|
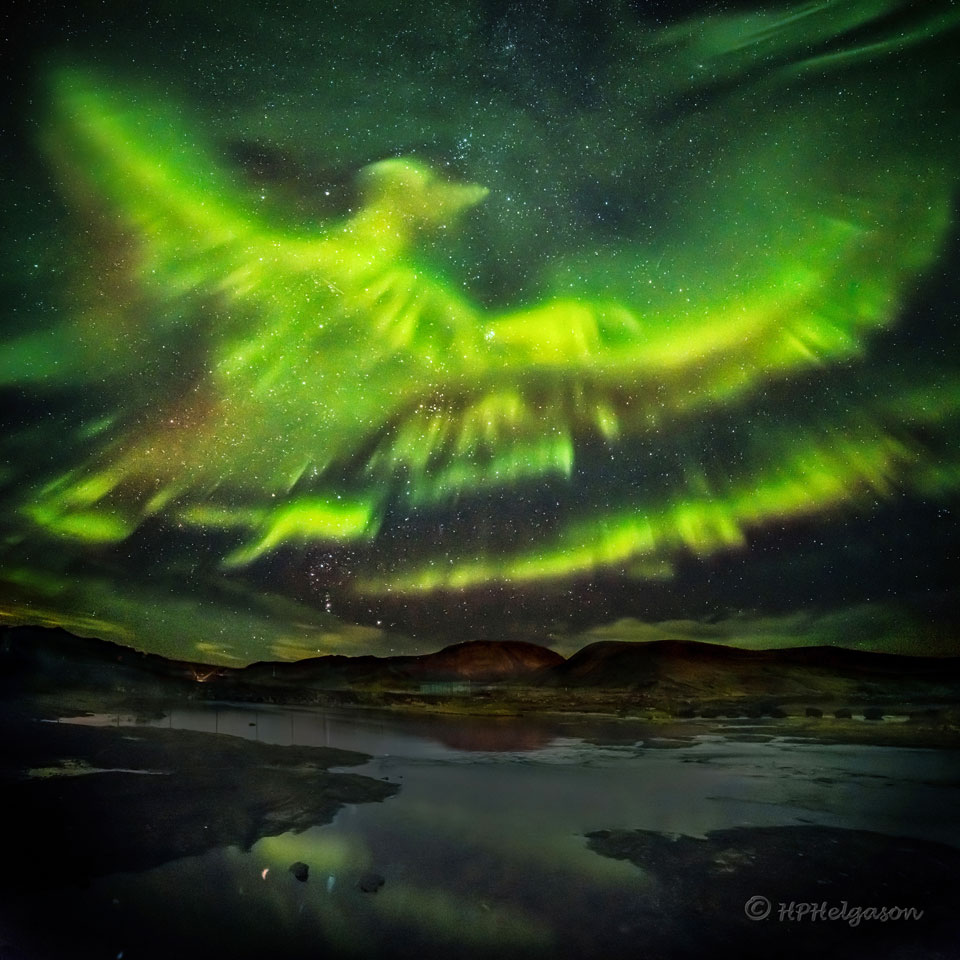
Re:NASA pics Date Posted:03/01/2021 7:38 AMCopy HTML Image Credit & Copyright: Hallgrimur P. Helgason; Rollover Annotation: Judy Schmidt Explanation: All of the other aurora watchers had gone home. By 3:30 am in Iceland, on a quiet September night, much of that night's auroras had died down. Suddenly, unexpectedly, a new burst of particles streamed down from space, lighting up the Earth's atmosphere once again. This time, surprisingly, pareidoliacally, the night lit up with an amazing shape reminiscent of a giant phoenix. With camera equipment at the ready, two quick sky images were taken, followed immediately by a third of the land. The mountain in the background is Helgafell, while the small foreground river is called Kaldá, both located about 30 kilometers north of Iceland's capital Reykjavík. Seasoned skywatchers will note that just above the mountain, toward the left, is the constellation of Orion, while the Pleiades star cluster is also visible just above the frame center. The 2016 aurora, which lasted only a minute and was soon gone forever -- would possibly be dismissed as an fanciful fable -- were it not captured in the featured, digitally-composed, image mosaic. |
|
|
Rockymz
|
Share to:





 #1210
#1210
|
|
Re:NASA pics Date Posted:02/01/2021 6:55 AMCopy HTML
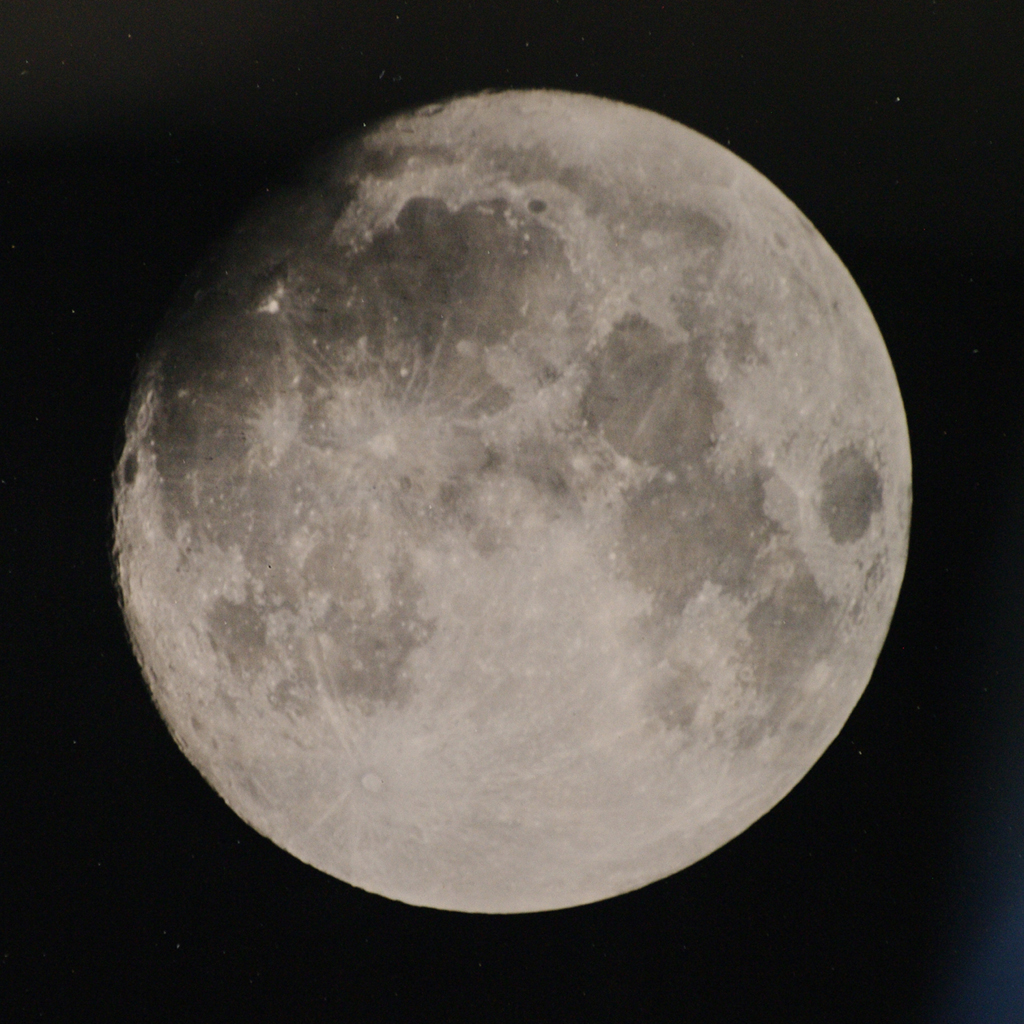
Image Credit & Copyright: Mike Smolinsky Explanation: In the mid 19th century, one of the first photographic technologies used to record the lunar surface was the wet-plate collodion process, notably employed by British astronomer Warren De la Rue. To capture an image, a thick, transparent mixture was used to coat a glass plate, sensitized with silver nitrate, exposed at the telescope, and then developed to create a negative image on the plate. To maintain photographic sensitivity, the entire process, from coating to exposure to developing, had to be completed before the plate dried, in a span of about 10 to 15 minutes. This modern version of a wet-plate collodion image celebrates lunar photography's early days, reproducing the process using modern chemicals to coat a glass plate from a 21st century hardware store. Captured last November 28 with an 8x10 view camera and backyard telescope, it faithfully records large craters, bright rays, and dark, smooth mare of the waxing gibbous Moon. Subsequently digitized, the image on the plate was 8.5 centimeters in diameter and exposed while tracking for 2 minutes. The wet plate's effective photographic sensitivity was about ISO 1. In your smart phone, the camera sensor probably has a photographic sensitivity range of ISO 100 to 6400 (and needs to be kept dry ...). |
|
|
Rockymz
|
Share to:





 #1211
#1211
|
|
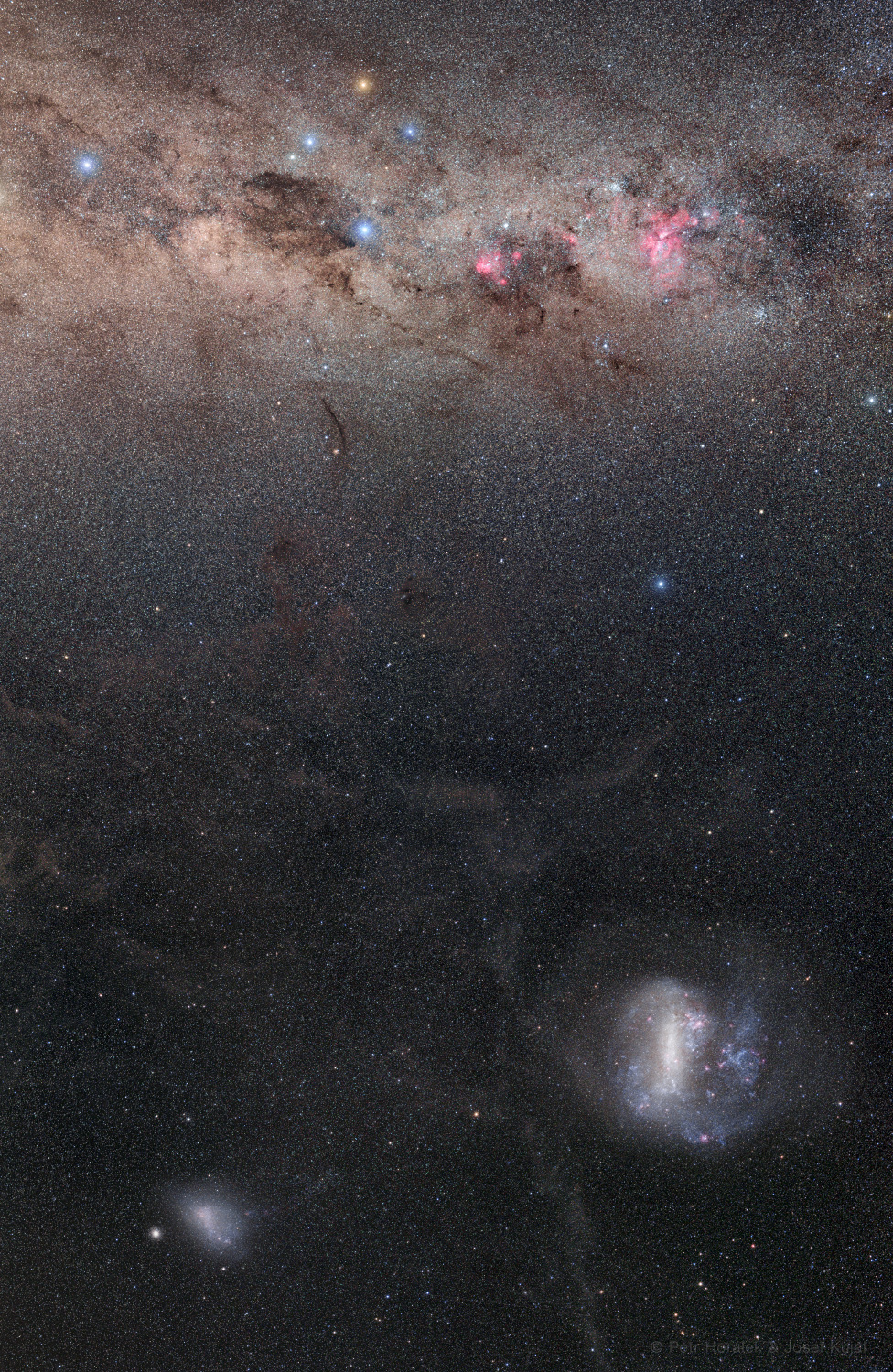
Re:NASA pics Date Posted:01/01/2021 8:29 AMCopy HTML Image Credit & Copyright: Petr Horalek, Josef Kujal Explanation: The South Celestial Pole is easy to spot in star trail images of the southern sky. The extension of Earth's axis of rotation to the south, it's at the center of all the southern star trail arcs. In this starry panorama streching about 60 degrees across deep southern skies the South Celestial Pole is somewhere near the middle though, flanked by bright galaxies and southern celestial gems. Across the top of the frame are the stars and nebulae along the plane of our own Milky Way Galaxy. Gamma Crucis, a yellowish giant star heads the Southern Cross near top center, with the dark expanse of the Coalsack nebula tucked under the cross arm on the left. Eta Carinae and the reddish glow of the Great Carina Nebula shine along the galactic plane near the right edge. At the bottom are the Large and Small Magellanic clouds, external galaxies in their own right and satellites of the mighty Milky Way. A line from Gamma Crucis through the blue star at the bottom of the southern cross, Alpha Crucis, points toward the South Celestial Pole, but where exactly is it? Just look for south pole star Sigma Octantis. Analog to Polaris the north pole star, Sigma Octantis is little over one degree fom the the South Celestial pole. |
|
|
Rockymz
|
Share to:





 #1212
#1212
|
|
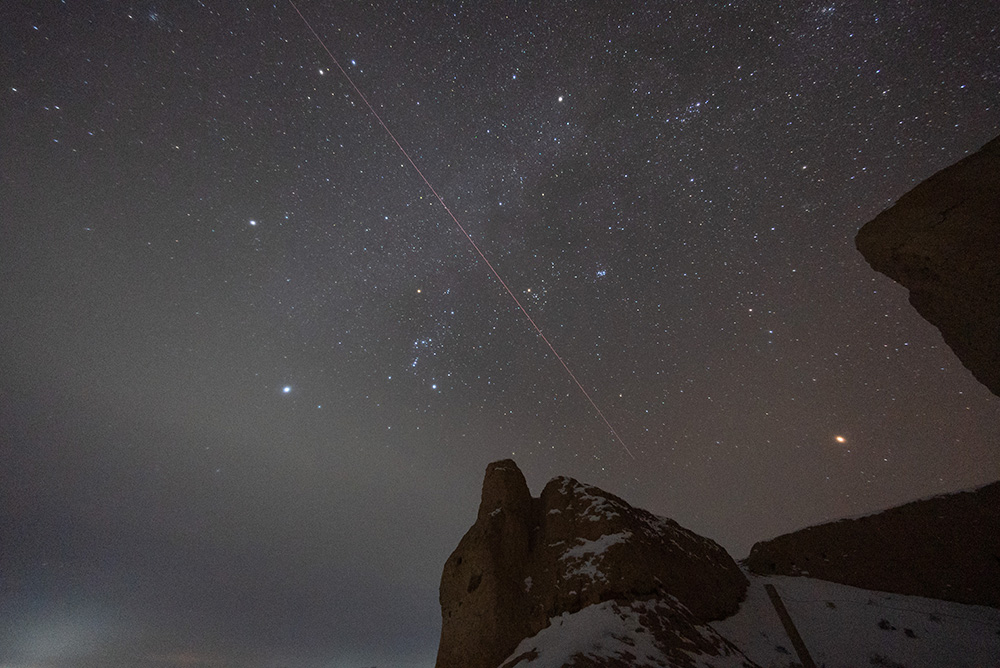
Re:NASA pics Date Posted:31/12/2020 8:02 AMCopy HTML Image Credit & Copyright: Zhuoxiao Wang Explanation: Familiar stars of a northern winter's night shine in this night skyview, taken near Zhangye, Gansu, China and the border with Inner Mongolia. During the early hours of December 17 Orion is near center in the single exposure that captures a fireball streaking across the sky, almost as bright as yellowish Mars shining on the right. Splitting Gemini's twin bright stars Castor and Pollux near the top of the frame, the fireball's trail and timing are consistent with the second skipping atmospheric entry of the Chang'e 5 mission's returner capsule. The returner capsule was successfully recovered after landing in Inner Mongolia, planet Earth with about 2 kilograms of lunar material on board. The lunar sample is thought to contain relatively youn |
|
|
Rockymz
|
Share to:





 #1213
#1213
|
|
Re:NASA pics Date Posted:30/12/2020 8:25 AMCopy HTML Image Credit & Copyright: Gyorgy Soponyai Explanation: An analemma is that figure-8 curve you get when you mark the position of the Sun at the same time each day for one year. But the trick to imaging an analemma of the Moon is to wait bit longer. On average the Moon returns to the same position in the sky about 50 minutes and 29 seconds later each day. So photograph the Moon 50 minutes 29 seconds later on successive days. Over one lunation or lunar month it will trace out an analemma-like curve as the Moon's actual position wanders due to its tilted and elliptical orbit. To create this composite image of a lunar analemma, astronomer Gyorgy Soponyai chose a lunar month from March 26 to April 18 with a good stretch of weather and a site close to home near Mogyorod, Hungary. Crescent lunar phases too thin and faint to capture around the New Moon are missing though. Facing southwest, the lights of Budapest are in the distance of the base image taken on March 27. |
|
|
Rockymz
|
Share to:





 #1214
#1214
|
|
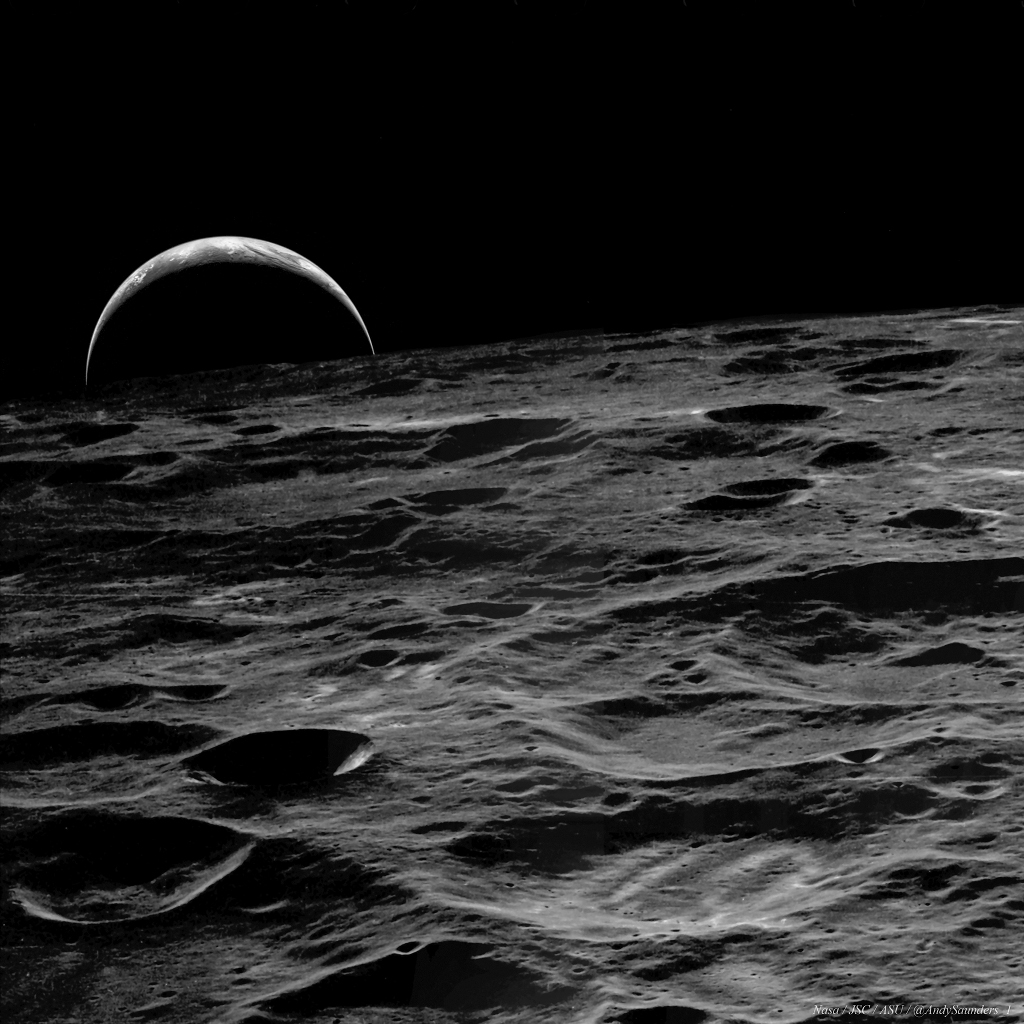
Re:NASA pics Date Posted:29/12/2020 7:37 AMCopy HTML Image Credit Apollo 14, NASA, JSC, ASU (Image Reprocessing: Andy Saunders) Explanation: When leaving lunar orbit in February 1971, the crew of Apollo 14 watched this Earthrise from their command module Kittyhawk. With Earth's sunlit crescent just peeking over the lunar horizon, the cratered terrain in the foreground is along the lunar farside. Of course, while orbiting the Moon, the crew could watch Earth rise and set, but the Earth hung stationary in the sky over Fra Mauro Base, their landing site on the lunar surface. Rock samples brought back by the Apollo 14 mission included a 20 pound rock nicknamed Big Bertha, later determined to contain a likely fragment of a meteorite from planet Earth. |
|
|
Rockymz
|
Share to:





 #1215
#1215
|
|
Re:NASA pics Date Posted:28/12/2020 8:20 AMCopy HTML
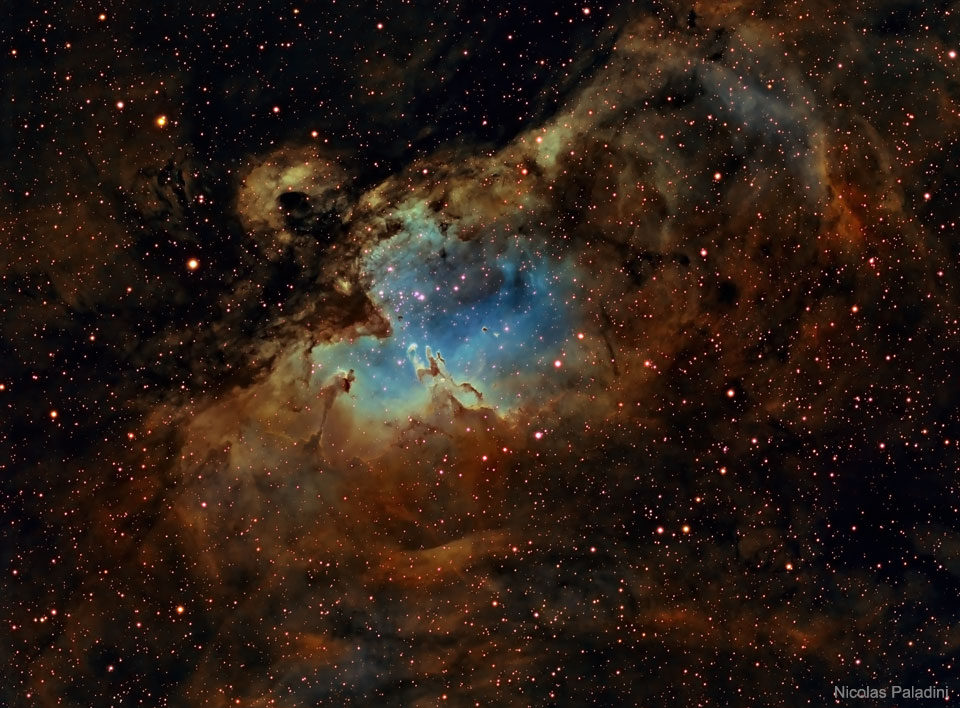
Image Credit & Copyright: Nicolas Paladini Explanation: From afar, the whole thing looks like an Eagle. A closer look at the Eagle Nebula, however, shows the bright region is actually a window into the center of a larger dark shell of dust. Through this window, a brightly-lit workshop appears where a whole open cluster of stars is being formed. In this cavity tall pillars and round globules of dark dust and cold molecular gas remain where stars are still forming. Already visible are several young bright blue stars whose light and winds are burning away and pushing back the remaining filaments and walls of gas and dust. The Eagle emission nebula, tagged M16, lies about 6500 light years away, spans about 20 light-years, and is visible with binoculars toward the constellation of the Serpent (Serpens). This picture involved over 12 hours of imaging and combines three specific emitted colors emitted by sulfur (colored as red), hydrogen (yellow), and oxygen (blue). |
|
|
Rockymz
|
Share to:





 #1216
#1216
|
|
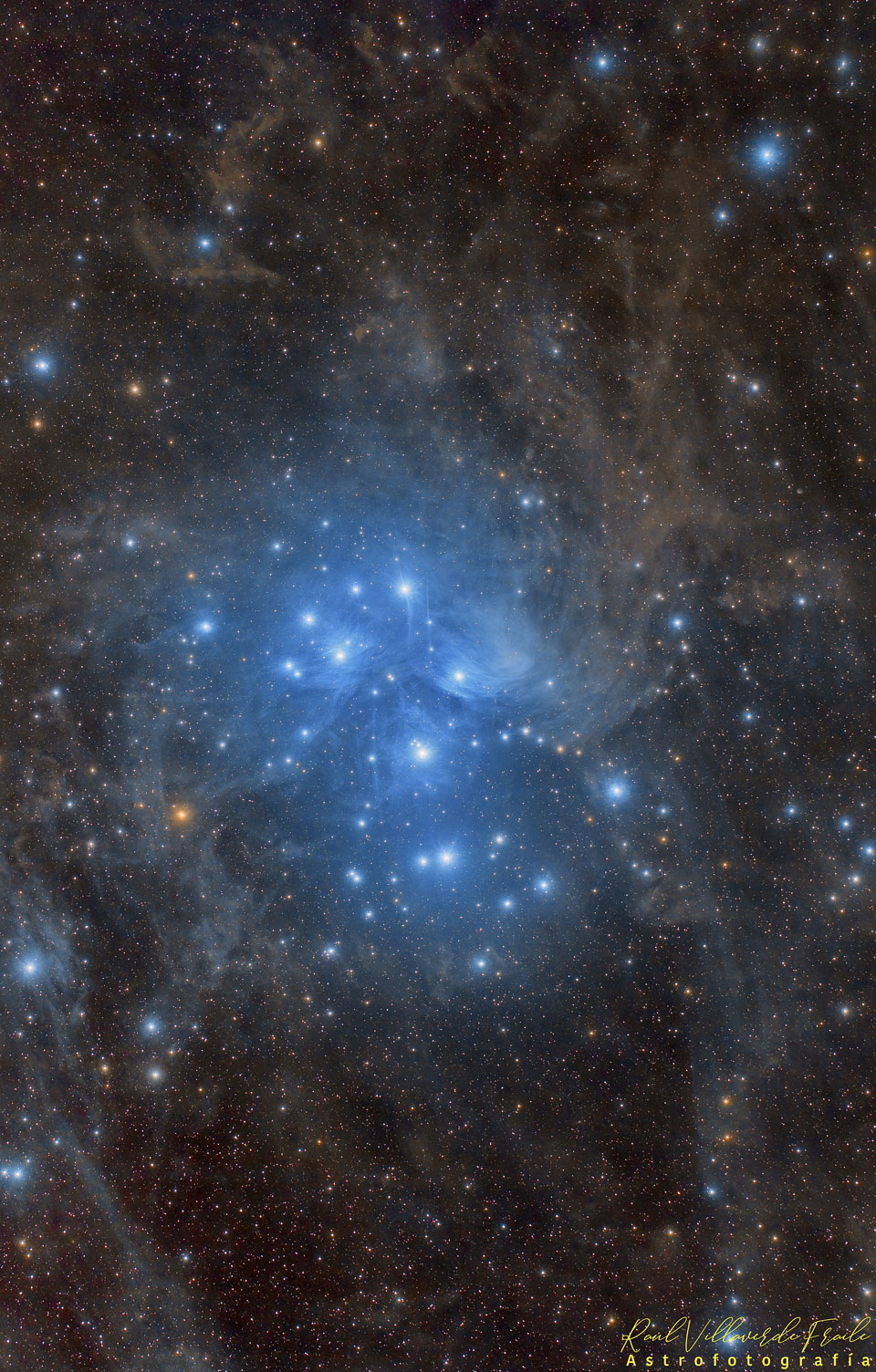
Re:NASA pics Date Posted:27/12/2020 8:43 AMCopy HTML Image Credit & Copyright: Raul Villaverde Fraile Explanation: Have you ever seen the Pleiades star cluster? Even if you have, you probably have never seen it as large and clear as this. Perhaps the most famous star cluster on the sky, the bright stars of the Pleiades can be seen without binoculars from even the depths of a light-polluted city. With a long exposure from a dark location, though, the dust cloud surrounding the Pleiades star cluster becomes very evident. The featured exposure covers a sky area several times the size of the full moon. Also known as the Seven Sisters and M45, the Pleiades lies about 400 light years away toward the constellation of the Bull (Taurus). A common legend with a modern twist is that one of the brighter stars faded since the cluster was named, leaving only six of the sister stars visible to the unaided eye. The actual number of Pleiades stars visible, however, may be more or less than seven, depending on the darkness of the surrounding sky and the clarity of the observer's eyesight. |
|
|
Rockymz
|
Share to:





 #1217
#1217
|
|
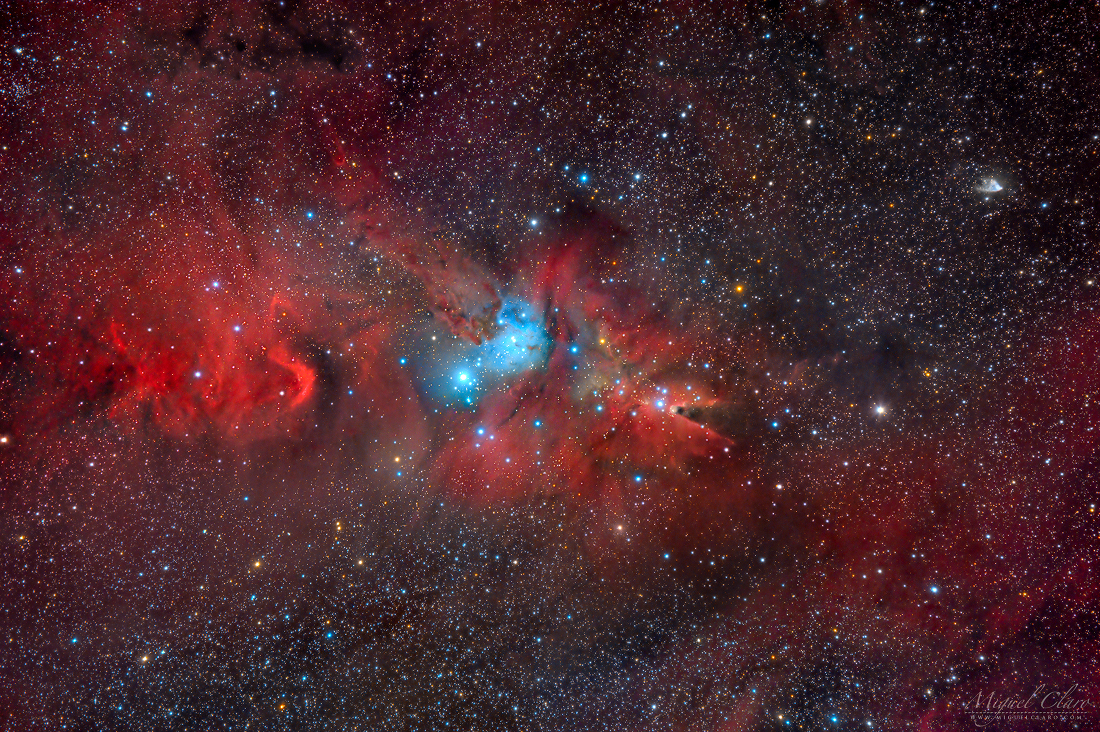
Re:NASA pics Date Posted:26/12/2020 8:50 AMCopy HTML Image Credit & Copyright: Miguel Claro (TWAN, Dark Sky Alqueva) Explanation: Clouds of glowing hydrogen gas fill this colorful skyscape in the faint but fanciful constellation Monoceros, the Unicorn. A star forming region cataloged as NGC 2264, the complex jumble of cosmic gas and dust is about 2,700 light-years distant and mixes reddish emission nebulae excited by energetic light from newborn stars with dark interstellar dust clouds. Where the otherwise obscuring dust clouds lie close to the hot, young stars they also reflect starlight, forming blue reflection nebulae. The telescopic image spans about 1.5 degrees or 3 full moons, covering nearly 80 light-years at the distance of NGC 2264. Its cast of cosmic characters includes the the Fox Fur Nebula, whose dusty, convoluted pelt lies left of center, bright variable star S Monocerotis immersed in the blue-tinted haze near center, and the Cone Nebula pointing in from the right side of the frame. Of course, the stars of NGC 2264 are also known as the Christmas Tree star cluster. The triangular tree shape is seen on its side here. Traced by brighter stars it has its apex at the Cone Nebula. The tree's broader base is centered near S Monocerotis. |
|
|
Rockymz
|
Share to:





 #1218
#1218
|
|
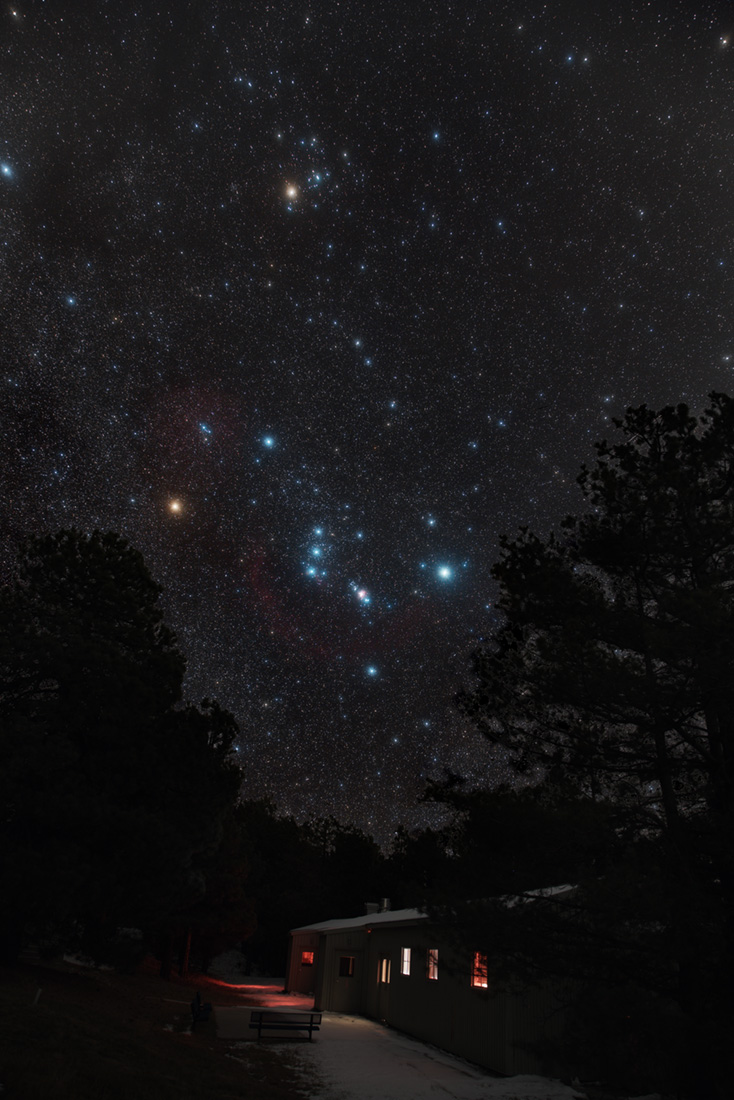
Re:NASA pics Date Posted:25/12/2020 7:59 AMCopy HTML Image Credit & Copyright: Adam Block Explanation: Orion always seems to come up sideways on northern winter evenings. Those familiar stars of the constellation of the Hunter are caught above the trees in this colorful night skyscape. Not a star at all but still visible to eye, the Great Nebula of Orion shines below the Hunter's belt stars. The camera's exposure reveals the stellar nursery's faint pinkish glow. Betelgeuse, giant star at Orion's shoulder, has the color of warm and cozy terrestrial lighting, but so does another familiar stellar giant, Aldebaran. Alpha star of the constellation Taurus the Bull, Aldebaran anchors the recognizable V-shape traced by the Hyades Cluster toward the top of the starry frame. |
|
|
Rockymz
|
Share to:





 #1219
#1219
|
|
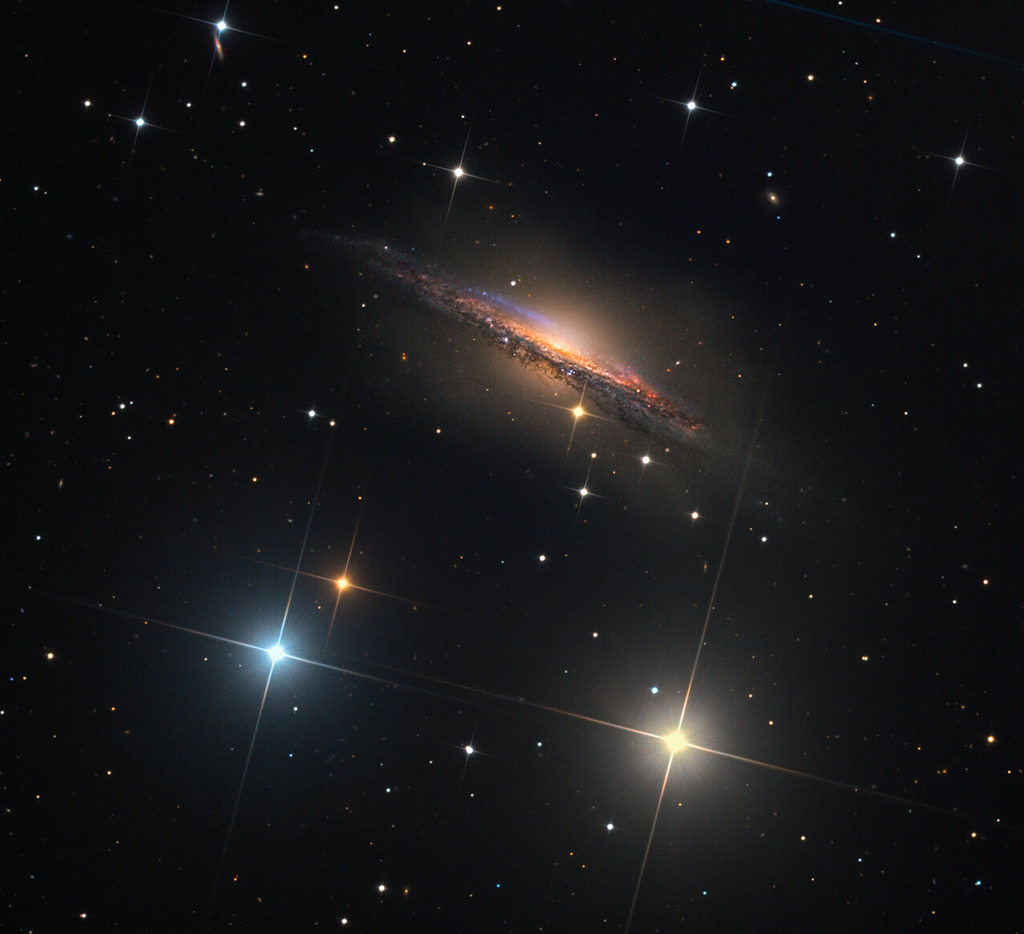
Re:NASA pics Date Posted:24/12/2020 8:36 AMCopy HTML Image Credit & Copyright: Martin Pugh Explanation: Big, beautiful spiral galaxy NGC 1055 is a dominant member of a small galaxy group a mere 60 million light-years away toward the aquatically intimidating constellation Cetus. Seen edge-on, the island universe spans over 100,000 light-years, a little larger than our own Milky Way galaxy. The colorful, spiky stars decorating this cosmic portrait of NGC 1055 are in the foreground, well within the Milky Way. But the telltale pinkish star forming regions are scattered through winding dust lanes along the distant galaxy's thin disk. With a smattering of even more distant background galaxies, the deep image also reveals a boxy halo that extends far above and below the central bluge and disk of NGC 1055. The halo itself is laced with faint, narrow structures, and could represent the mixed and spread out debris from a satellite galaxy disrupted by the larger spiral some 10 billion years ago. |
|
|
Rockymz
|
Share to:





 #1220
#1220
|
|
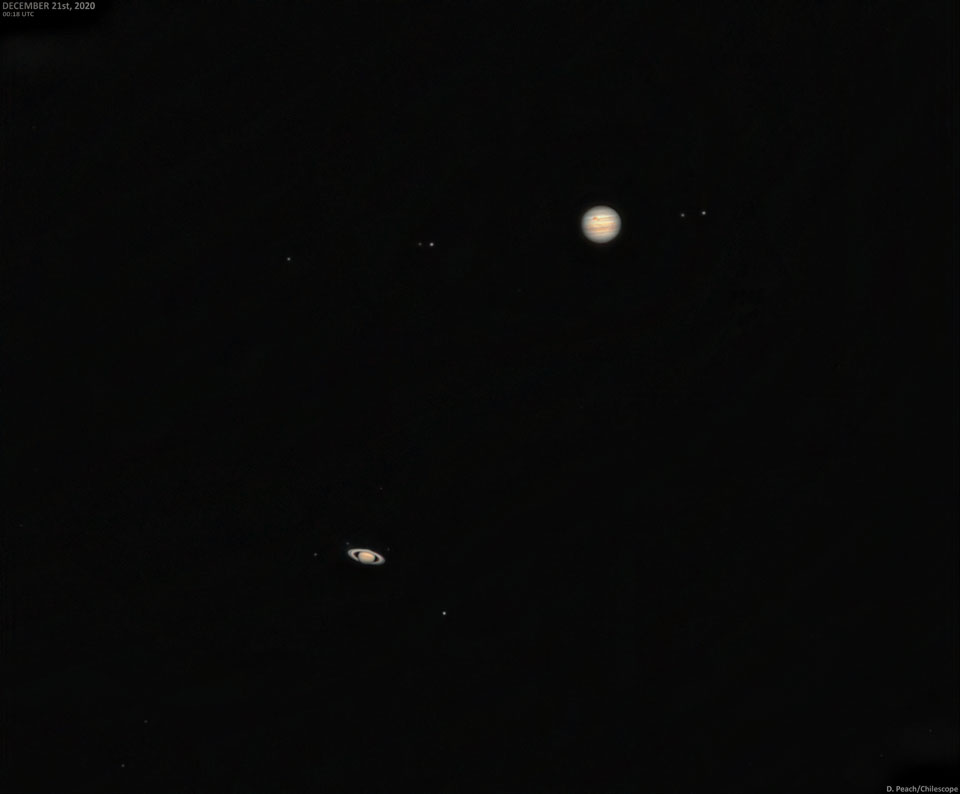
Re:NASA pics Date Posted:23/12/2020 7:09 AMCopy HTML Image Credit & Copyright: Damian Peach Explanation: It was time for their close-up. Two days ago Jupiter and Saturn passed a tenth of a degree from each other in what is known a Great Conjunction. Although the two planets pass each other on the sky every 20 years, this was the closest pass in nearly four centuries. Taken early in day of the Great Conjunction, the featured multiple-exposure combination captures not only both giant planets in a single frame, but also Jupiter's four largest moons (left to right) Callisto, Ganymede, Io, and Europa -- and Saturn's largest moon Titan. If you look very closely, the clear Chilescope image even captures Jupiter's Great Red Spot. The now-separating planets can still be seen remarkably close -- within about a degree -- as they set just after the Sun, toward the west, each night for the remainder of the year. |
|
|
Rockymz
|
Share to:





 #1221
#1221
|
|
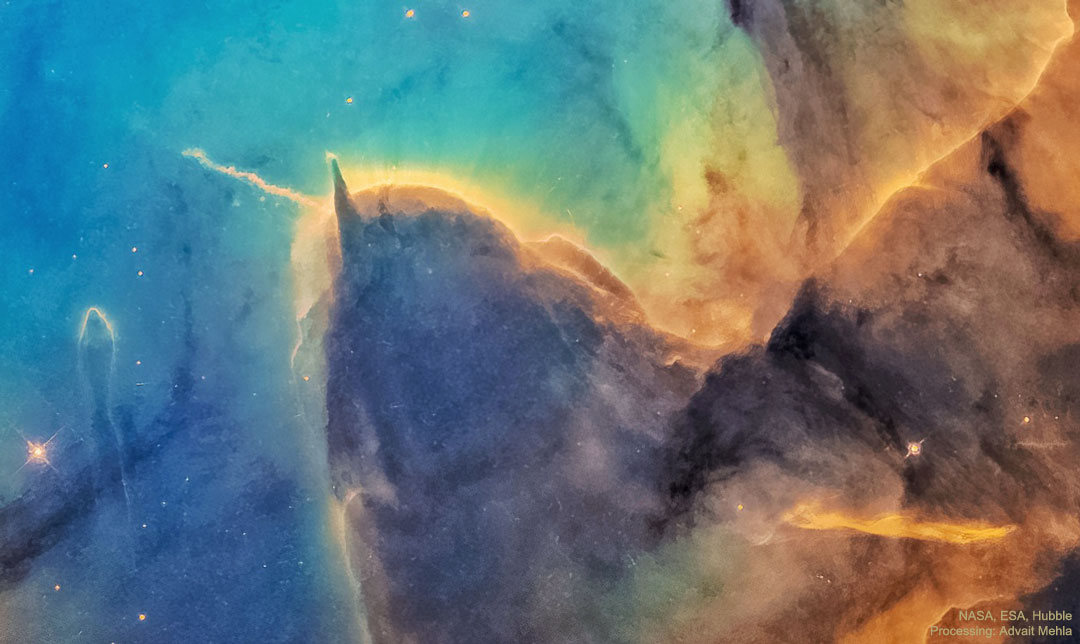
Re:NASA pics Date Posted:22/12/2020 6:51 AMCopy HTML Image Credit: NASA, ESA, Hubble Space Telescope, HLA; Processing: Advait Mehla Explanation: Dust pillars are like interstellar mountains. They survive because they are more dense than their surroundings, but they are being slowly eroded away by a hostile environment. Visible in the featured picture is the end of a huge gas and dust pillar in the Trifid Nebula (M20), punctuated by a smaller pillar pointing up and an unusual jet pointing to the left. Many of the dots are newly formed low-mass stars. A star near the small pillar's end is slowly being stripped of its accreting gas by radiation from a tremendously brighter star situated off the top of the image. The jet extends nearly a light-year and would not be visible without external illumination. As gas and dust evaporate from the pillars, the hidden stellar source of this jet will likely be uncovered, possibly over the next 20,000 years. |
|
|
Rockymz
|
Share to:





 #1222
#1222
|
|
Re:NASA pics Date Posted:21/12/2020 7:04 AMCopy HTML Image Credit & Copyright: Zaid M. Al-Abbadi Explanation: Does the Sun always rise in the same direction? No. As the months change, the direction toward the rising Sun changes, too. The featured image shows the direction of sunrise every month during 2019 as seen from near the city of Amman, Jordan. The camera in the image is always facing due east, with north toward the left and south toward the right. Although the Sun always rises in the east in general, it rises furthest to the south of east on the December solstice, and furthest north of east on the June solstice. Today is the December solstice, the day of least sunlight in the Northern Hemisphere and of most sunlight in the Southern Hemisphere. In many countries, the December Solstice is considered an official change in season: for example the first day of winter in the North. Solar heating and stored energy in the Earth's surface and atmosphere are near their lowest during winter, making the winter months usually the coldest of the year. On the brighter side, in the north, daylight hours will now increase every day from until June. |
|
|
Rockymz
|
Share to:





 #1223
#1223
|
|
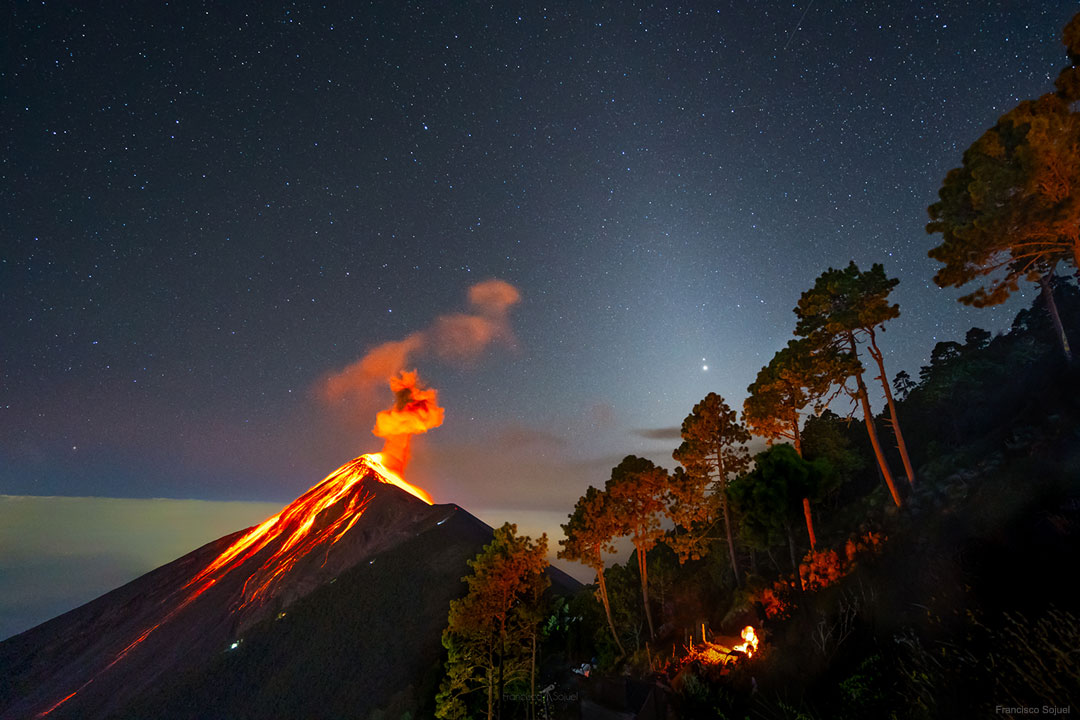
Re:NASA pics Date Posted:20/12/2020 8:11 AMCopy HTML Image Credit & Copyright: Francisco Sojuel Explanation: Where can I see the Great Conjunction? Near where the Sun just set. Directionally, this close passing of Jupiter and Saturn will be toward the southwest. Since the planetary pair, the Sun, and the Earth are nearly in a geometric straight line, the planets will be seen to set just where the Sun had set -- from every location on Earth. When can I see the Great Conjunction? Just after sunset. Since the two planets are so near the Sun directionally, they always appear in the sky near the Sun, but can best be seen when the Earth blocks the Sun but not the planets: sunset. Soon thereafter, Jupiter and Saturn will also set, so don't be late! Is tomorrow night the only night that I can see the Great Conjunction? Tomorrow night the jovian giants will appear the closest, but on any night over the next few days they will appear unusually close. Technically, the closest pass happens on 21 December at 18:20 UTC. Will there be an erupting volcano on the horizon near the Great Conjunction? Yes, for example if you live in Guatemala where the featured image was taken. Otherwise, generally, no. In the featured image captured last week, Jupiter and Saturn are visible toward the right, just above a tree, and bathed in the diffuse glow of zodiacal light. |
|
|
Rockymz
|
Share to:





 #1224
#1224
|
|
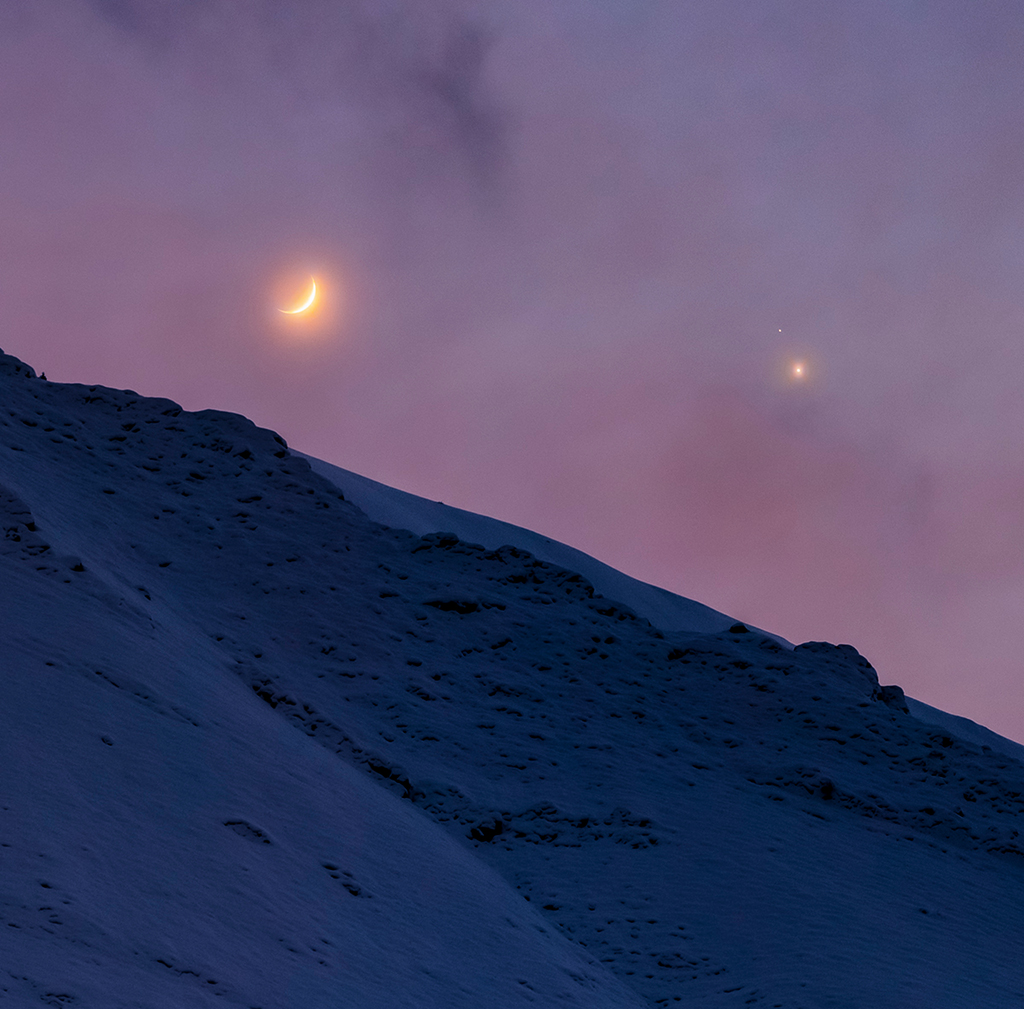
Re:NASA pics Date Posted:19/12/2020 6:40 AMCopy HTML Image Credit & Copyright: Alireza Vafa Explanation: How close will Jupiter and Saturn be at their Great Conjunction? Consider this beautiful triple conjunction of Moon, Jupiter and Saturn captured through clouds in the wintry twilight. The telephoto view looks toward the western horizon and the Alborz Mountains in Iran after sunset on December 17. The celestial gathering makes it easy to see Jupiter and fainter Saturn are separated on that date by roughly the diameter of the waxing crescent Moon. On the day of their Great Conjunction, solstice day December 21, Jupiter and Saturn may seem to nearly merge though. In their closest conjunction in 400 years they will be separated on the sky by only about 1/5 the apparent diameter of the Moon. By then the two largest worlds in the Solar System and their moons will be sharing the same field of view in telescopes around planet Earth. |
|
|
Rockymz
|
Share to:





 #1225
#1225
|
|
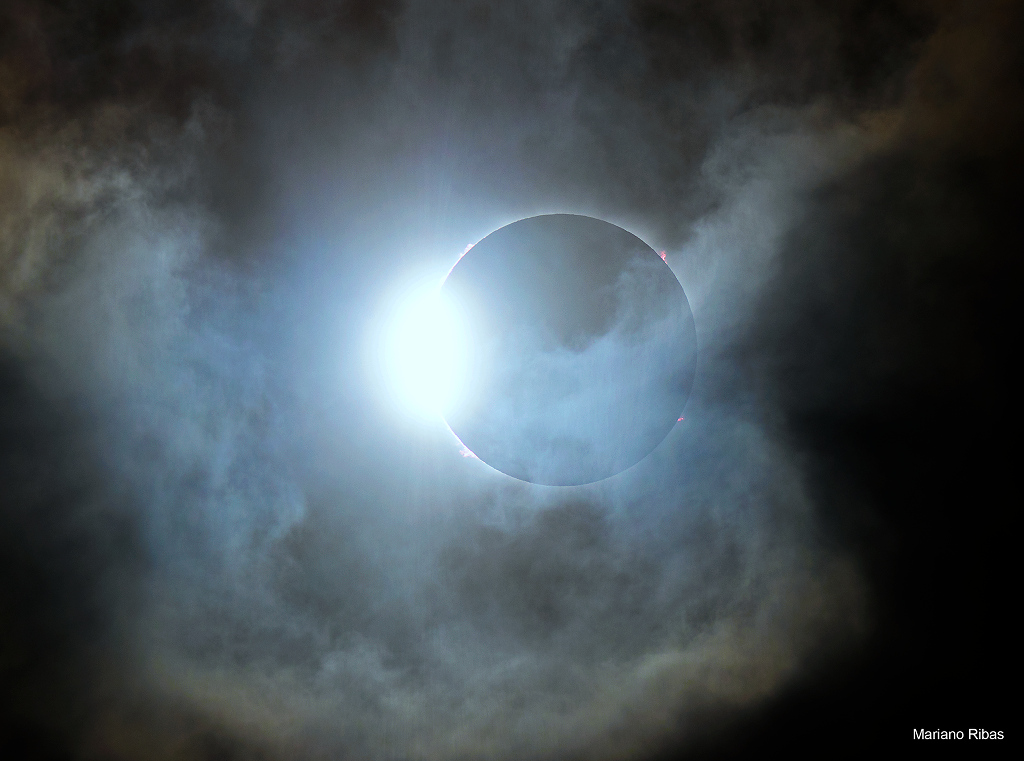
Re:NASA pics Date Posted:18/12/2020 7:47 AMCopy HTML Image Credit & Copyright: Mariano Ribas (Planetario de la Ciudad de Buenos Aires) Explanation: When the shadow of the Moon raced across planet Earth's southern hemisphere on December 14, sky watchers along the shadow's dark central path were treated to the only total solar eclipse of 2020. During the New Moon's shadow play this glistening diamond ring was seen for a moment, even in cloudy skies. Known as the diamond ring effect, the transient spectacle actually happens twice. Just before and immediately after totality, a thin sliver of solar disk visible behind the Moon's edge creates the appearance of a shiny jewel set in a dark ring. This dramatic snapshot from the path of totality in northern Patagonia, Argentina captures this eclipse's second diamond ring, along with striking solar prominences lofted beyond the edge of the Moon's silhoutte. |
|
|
Rockymz
|
Share to:





 #1226
#1226
|
|
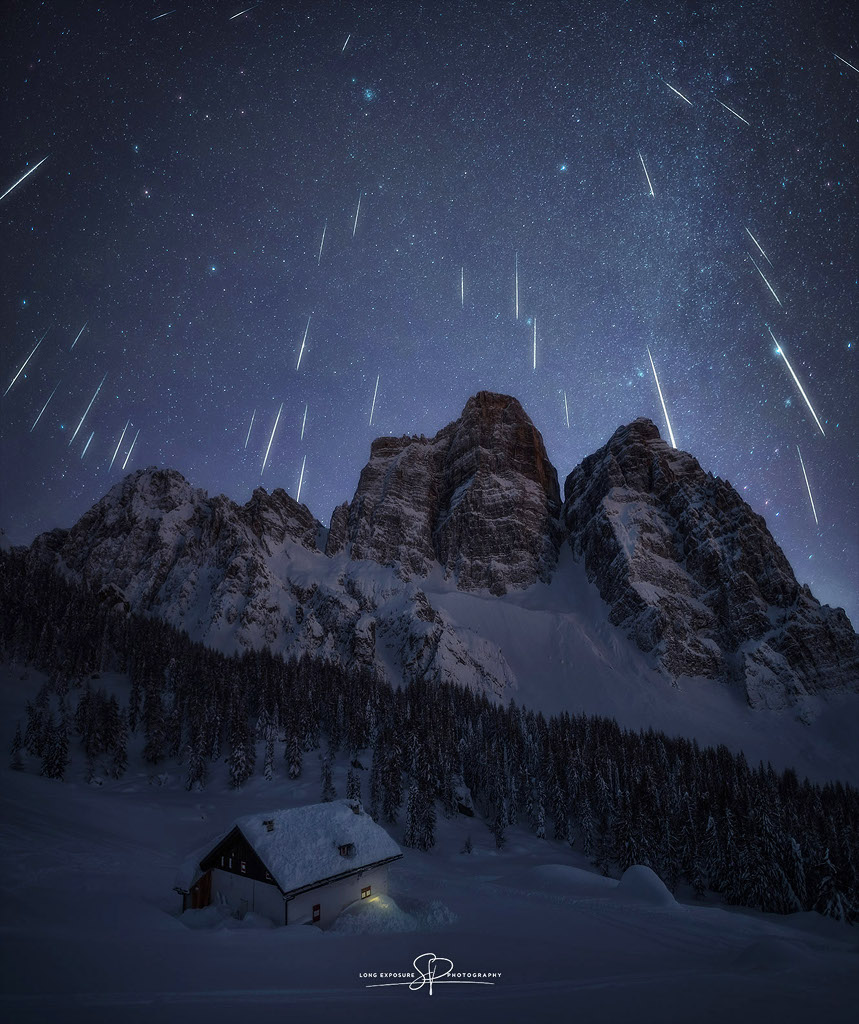
Re:NASA pics Date Posted:17/12/2020 8:03 AMCopy HTML Image Credit & Copyright: Stefano Pellegrini Explanation: Taken over the course of an hour shortly after local midnight on December 13, 35 exposures were used to create this postcard from Earth. The composited night scene spans dark skies above the snowy Italian Dolomites during our fair planet's annual Geminid meteor shower. Sirius, alpha star of Canis Major and the brightest star in the night, is grazed by a meteor streak on the right. The Praesepe star cluster, also known as M44 or the Beehive cluster, itself contains about a thousand stars but appears as a smudge of light far above the southern alpine peaks near the top. The shower's radiant is off the top of the frame though, near Castor and Pollux the twin stars of Gemini. The radiant effect is due to perspective as the parallel meteor tracks appear to converge in the distance. As Earth sweeps through the dust trail of asteroid 3200 Phaethon, the dust that creates Gemini's meteors enters Earth's atmosphere traveling at about 22 kilometers per second |
|
|
Rockymz
|
Share to:





 #1227
#1227
|
|
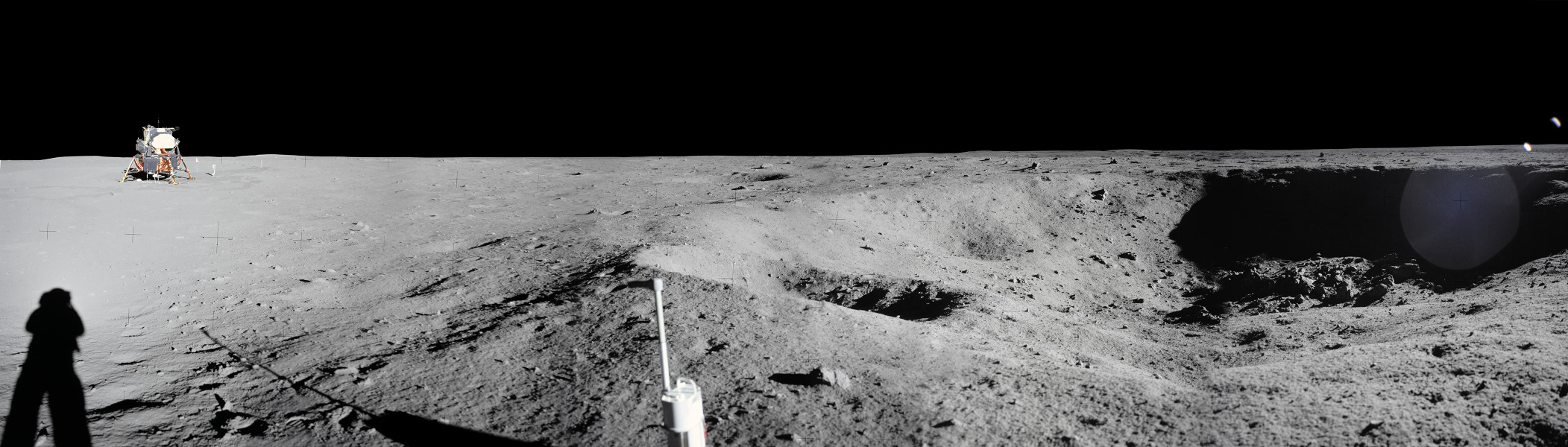
Re:NASA pics Date Posted:16/12/2020 7:59 AMCopy HTML Image Credit: Neil Armstrong, Apollo 11, NASA Explanation: On July 20, 1969 the Apollo 11 lunar module Eagle safely touched down on the Moon. It landed near the southwestern corner of the Moon's Mare Tranquillitatis at a landing site dubbed Tranquility Base. This panoramic view of Tranquility Base was constructed from the historic photos taken from the lunar surface. On the far left astronaut Neil Armstrong casts a long shadow with Sun is at his back and the Eagle resting about 60 meters away ( AS11-40-5961). He stands near the rim of 30 meter-diameter Little West crater seen here to the right ( AS11-40-5954). Also visible in the foreground is the top of the camera intended for taking stereo close-ups of the lunar surface. |
|
|
Rockymz
|
Share to:





 #1228
#1228
|
|
Re:NASA pics Date Posted:15/12/2020 8:03 AMCopy HTML Illustration Credit & Copyright: Sebastian Voltmer Explanation: It's happening. Saturn and Jupiter are moving closer and will soon appear in almost exactly the same direction. Coincidentally, on the night of the December solstice -- the longest night of the year in the north and the longest day in the south -- the long-awaited Great Conjunction will occur. Then, about six days from now, Saturn and Jupiter will be right next to each other -- as they are every 20 years. But this juxtaposition is not just any Great Conjunction -- it will be the closest since 1623 because the two planetary giants will pass only 1/10th of a degree from each other -- well less than the apparent diameter of a full moon. In the next few days a crescent moon will also pass a few degrees away from the converging planets and give a preliminary opportunity for iconic photos. The featured illustration shows the approach of Saturn and Jupiter during November and December over the French Alps. |
|
|
Rockymz
|
Share to:





 #1229
#1229
|
|
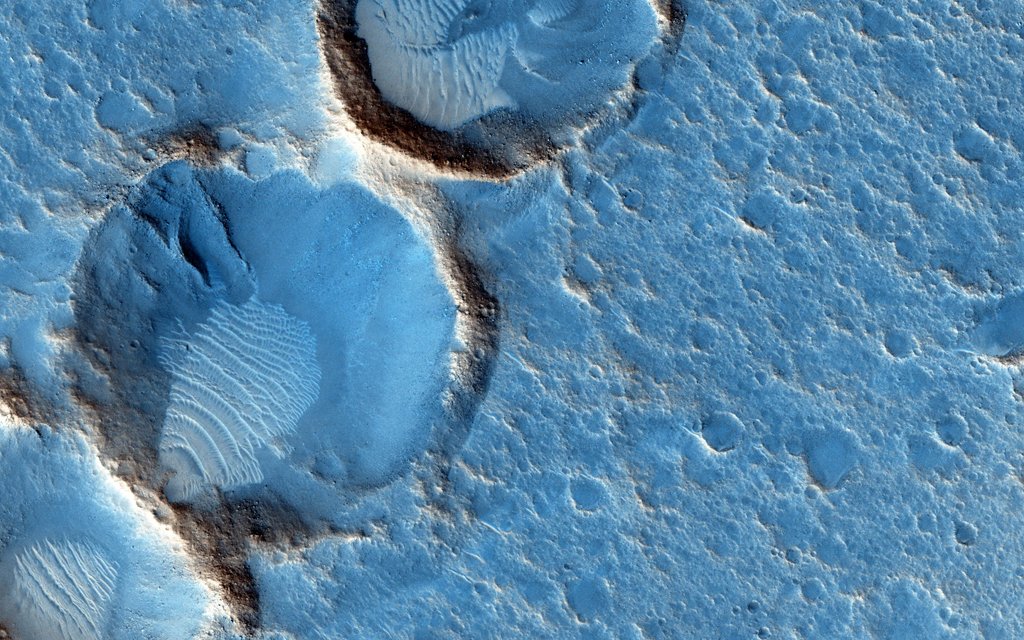
Re:NASA pics Date Posted:14/12/2020 7:50 AMCopy HTML Image Credit: HiRISE, MRO, LPL (U. Arizona), NASA Explanation: This close-up from the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter's HiRISE camera shows weathered craters and windblown deposits in southern Acidalia Planitia. A striking shade of blue in standard HiRISE image colors, to the human eye the area would probably look grey or a little reddish. But human eyes have not gazed across this terrain, unless you count the eyes of NASA astronauts in the scifi novel The Martian by Andy Weir. The novel chronicles the adventures of Mark Watney, an astronaut stranded at the fictional Mars mission Ares 3 landing site corresponding to the coordinates of this cropped HiRISE frame. For scale Watney's 6-meter-diameter habitat at the site would be about 1/10th the diameter of the large crater. Of course, the Ares 3 landing coordinates are only about 800 kilometers north of the (real life) Carl Sagan Memorial Station, the 1997 Pathfinder landing site. |
|
|
Rockymz
|
Share to:





 #1230
#1230
|
|
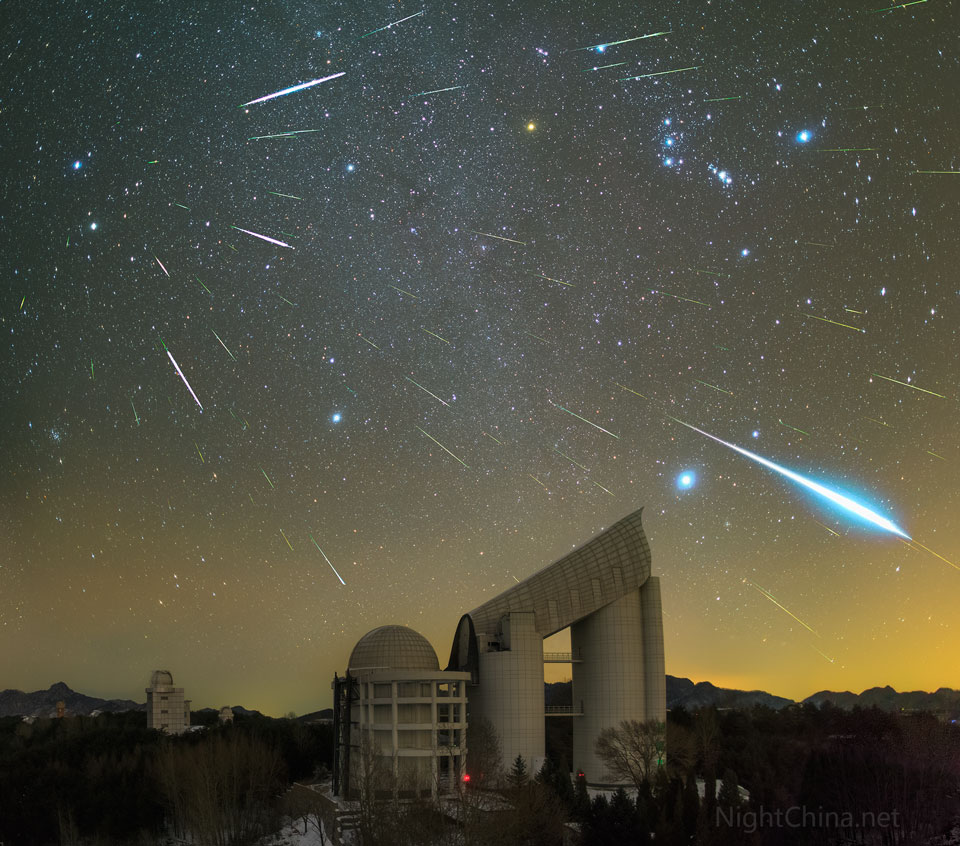
Re:NASA pics Date Posted:13/12/2020 8:57 AMCopy HTML Image Credit & Copyright: Steed Yu and NightChina.net Explanation: Where do Geminid meteors come from? In terms of location on the sky, as the featured image composite beautifully demonstrates, the sand-sized bits of rock that create the streaks of the Geminids meteor shower appear to flow out from the constellation of Gemini. In terms of parent body, Solar System trajectories point to the asteroid 3200 Phaethon -- but this results in a bit of a mystery since that unusual object appears mostly dormant. Perhaps, 3200 Phaethon undergoes greater dust-liberating events than we know. Over 50 meteors including a bright fireball were captured during the peak of the 2015 Geminids Meteor Shower streaking above Xinglong Observatory in China. The Geminids of December are one of the most predictable and active meteor showers. This year's Geminids peak tonight and should be particularly good because, in part, the nearly new Moon will only rise toward dawn and so not brighten the sky. |